BinaryAlert
Serverless real-time and retroactive malware detection
1,149

By Austin Byers, @mimeframe, Daimon Greaves
Serverless real-time and retroactive malware detection
BinaryAlert is an open-source serverless AWS pipeline where any file uploaded to an S3 bucket is immediately scanned with a configurable set of YARA rules. An alert will fire as soon as any match is found, giving an incident response team the ability to quickly contain the threat before it spreads.
Features
- Built with Amazon Web Services (AWS): An AWS account is all you need to deploy BinaryAlert.
- Broad YARA Support: Add your own YARA rules and/or automatically clone them from third-party repos.
- Real-Time: Files uploaded to BinaryAlert (S3 bucket) are immediately queued for analysis.
- Serverless: All computation is handled by Lambda functions. No servers to manage means stronger security and automatic scaling!
- Infrastructure-as-Code: The entire infrastructure is described with Terraform configuration files, enabling anyone to deploy BinaryAlert in a matter of minutes with a single command.
- Retroactive Analysis: After updating the YARA ruleset, BinaryAlert will retroactively scan the entire file corpus to find any new matches.
- Easily Configurable: BinaryAlert configuration is managed in a single Terraform variables file.
- Quality Code: Written in Python3 with unit tests and linting to ensure a clean and reliable codebase.
- Low Cost: The AWS bill is based only on how many files are analyzed.
Architecture
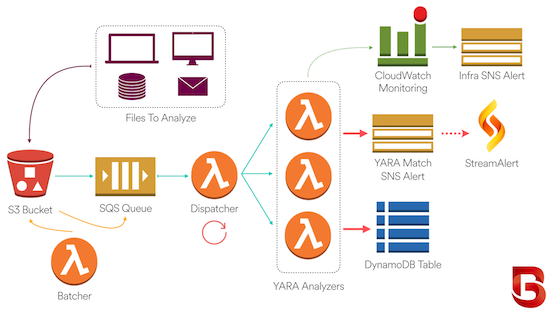
- The organization collects files and delivers them to their BinaryAlert S3 bucket. Files of interest could include executable binaries, email attachments, documents, etc.
- Every file uploaded to the S3 bucket is immediately queued for analysis.
- A dispatching Lambda function runs every minute, grouping files into batches and invoking up to dozens of analyzers in parallel.
- Each analyzer scans its files using a list of pre-compiled YARA rules.
- YARA matches are saved to DynamoDB and an alert is sent to an SNS topic. We use StreamAlert to dispatch these alerts, but other organizations can instead consume the alerts via email or any other supported SNS subscription.
- For retroactive analysis, a batching Lambda function enqueues the entire S3 bucket to be re-analyzed.
- Configurable CloudWatch alarms will trigger if any BinaryAlert component is behaving abnormally. This will notify a different SNS topic than the one used for YARA match alerts.